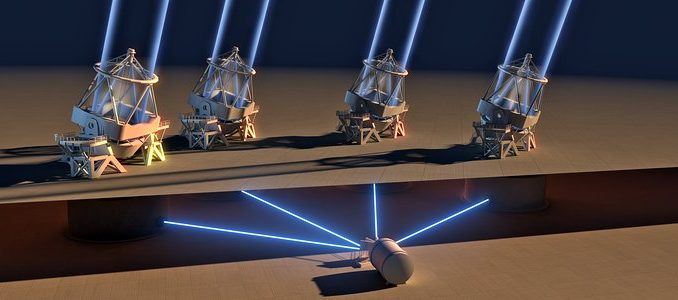
The ESPRESSO instrument on the European Southern Observatoty (ESO) Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile has used the combined light of all four of its 8.2-meter Unit Telescopes for the first time. Combining light from the Unit Telescopes in this way makes the VLT the largest optical telescope in existence in terms of collecting area.
One of the original design goals of the VLT was for its four Unit Telescopes (UTs) to work together to create a single giant telescope. With the first light of the ESPRESSO spectrograph using the four-Unit-Telescope mode of the VLT, this milestone has now been reached.
After extensive preparations by the ESPRESSO consortium (led by the Astronomical Observatory of the University of Geneva, with the participation of research centers from Italy, Portugal, Spain and Switzerland) and ESO staff, ESO’s Director General Xavier Barcons initiated this historic astronomical observation with the push of a button in the control room.
ESPRESSO instrument scientist at ESO, Gaspare Lo Curto, explains the historical significance of this event: “ESO has realized a dream that dates back to the time when the VLT was conceived in the 1980s: combining the light of all four Unit Telescopes on Cerro Paranal to feed a single instrument!”
When all four 8.2-metre Unit Telescopes combine their light-collecting power to feed a single instrument, the VLT effectively becomes the largest optical telescope in the world in terms of collecting area.
Two of the main scientific goals of ESPRESSO are the discovery and characterization of Earth-like planets and the search for possible variability of the fundamental constants of physics. The latter experiments in particular require the observation of distant and faint quasars, and this science goal will benefit the most from combining the light from all four Unit Telescopes in ESPRESSO. Both rely on the ultra-high stability of the instrument and an extremely stable reference light source.
Due to the complexity involved, the combination of light from all four Unit Telescopes in this way, at what is known as an “incoherent focus”, had not been implemented until now. However, space for it was built into the telescopes and the underground structure of the mountaintop from the start.
A system of mirrors, prisms and lenses transmits the light from each VLT Unit Telescope to the ESPRESSO spectrograph up to 69 meters away. Thanks to these complex optics, ESPRESSO can either collect the light from up to all four Unit Telescopes together, increasing its light-gathering power, or alternatively receive light from any one of the Unit Telescopes independently, allowing for more flexible usage of observing time. ESPRESSO was specially developed to exploit this infrastructure.
Light from the four Unit Telescopes is routinely brought together in the VLT Interferometer for the study of extremely fine detail in comparatively bright objects. But interferometry, which combines the beams “coherently,” cannot exploit the huge light-gathering potential of the combined telescopes to study faint objects.
Feeding the combined light into a single instrument will give astronomers access to information never previously available. This new facility is a game-changer for astronomy with high-resolution spectrographs. It makes use of novel concepts, such as wavelength calibration aided by a laser frequency comb, providing unprecedented precision and repeatability, and now the capability to join together the light-collecting power of the four individual Unit Telescopes.

Be the first to comment