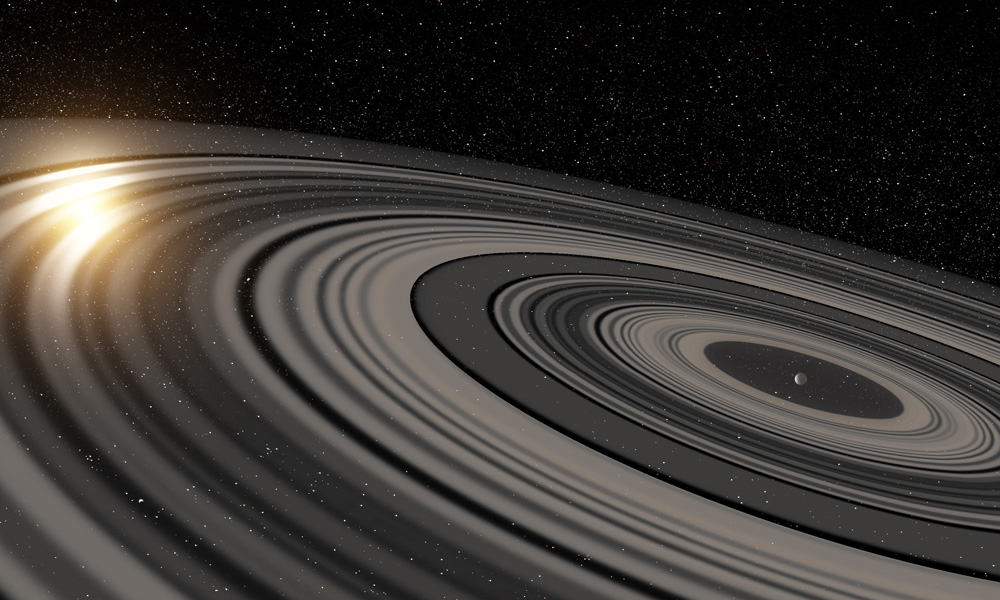

 Astronomers at the Leiden Observatory (The Netherlands) and the University of Rochester (USA) have discovered that the ring system that they see eclipse the very young Sun-like star J1407 is of enormous proportions, much larger and heavier than the ring system of Saturn. The ring system—the first of its kind to be found outside our solar system—was discovered in 2012 by a team led by Rochester’s Eric Mamajek.
Astronomers at the Leiden Observatory (The Netherlands) and the University of Rochester (USA) have discovered that the ring system that they see eclipse the very young Sun-like star J1407 is of enormous proportions, much larger and heavier than the ring system of Saturn. The ring system—the first of its kind to be found outside our solar system—was discovered in 2012 by a team led by Rochester’s Eric Mamajek.
The astronomers analyzed data from the SuperWASP project—a survey designed to detect gas giants that move in front of their parent star. In 2012, Mamajek and colleagues at the University of Rochester reported the discovery of the young star J1407 and the unusual eclipses, and proposed that they were caused by a moon-forming disk around a young giant planet or brown dwarf.
A new analysis of the data, led by Leiden’s Matthew Kenworthy, shows that the ring system consists of over 30 rings, each of them tens of millions of kilometers in diameter. Furthermore, they found gaps in the rings, indicating that satellites (“exomoons”) may have formed. The result has been accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal.
“The details that we see in the light curve are incredible. The eclipse lasted for several weeks, but you see rapid changes on time scales of tens of minutes as a result of fine structures in the rings,” says Kenworthy. “The star is much too far away to observe the rings directly, but we could make a detailed model based on the rapid brightness variations in the starlight passing through the ring system. If we could replace Saturn’s rings with the rings around J1407b, they would be easily visible at night and be many times larger than the full Moon.”
“This planet is much larger than Jupiter or Saturn, and its ring system is roughly 200 times larger than Saturn’s rings are today,” said co-author Mamajek, professor of physics and astronomy at the University of Rochester. “You could think of it as kind of a super Saturn.”
In another recent study also led by Kenworthy, adaptive optics and Doppler spectroscopy were used to estimate the mass of the ringed object. Their conclusions based on these and previous papers on the intriguing system J1407 is that the companion is likely to be a giant planet—not yet seen—with a gigantic ring system responsible for the repeated dimming of J1407’s light.
The light curve tells astronomers that the diameter of the ring system is nearly 120 million kilometers, more than two hundred times as large as the rings of Saturn. The ring system likely contains roughly an Earth’s worth of mass in light-obscuring dust particles.
Mamajek puts into context how much material is contained in these disks and rings. “If you were to grind up the four large Galilean moons of Jupiter into dust and ice and spread out the material over their orbits in a ring around Jupiter, the ring would be so opaque to light that a distant observer that saw the ring pass in front of the Sun would see a very deep, multi-day eclipse,” Mamajek says. “In the case of J1407, we see the rings blocking as much as 95 percent of the light of this young Sun-like star for days, so there is a lot of material there that could then form satellites.”
Astronomers expect that the rings will become thinner in the next several million years and eventually disappear as satellites form from the material in the disks.
photo credit – U of R Newscenter

Be the first to comment